ProZ.com translation contests » |
Source text in English 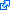
The winning entry has been announced in this pair.There were 8 entries submitted in this pair during the submission phase. The winning entry was determined based on finals round voting by peers.Competition in this pair is now closed. |
Entries (8 total) — Expand all entries
अनेक वर्षों के दौरान, इस विषय में बहुत ज्यादा शोर किए बगैर न्यूयार्क में अधिकारियों ने ज्यादातर नियंत्रण बटनों को निष्क्रिय कर दिया जो कभी पदयात्रिययों के लिए क्रासिंग लाइटों को संचालित करते थे। उन्होंने निर्णय लिया कि कंप्युटरीकृत टाइमरों ने लगभग हमेशा अच्छा कार्य किया था। 2004 तक ऐसे 3,250 बटनों में से 750 से भी कम कार्य कर रहे थे। परंतु शहर के शासन ने निष्क्रिय बटनों को वहां से नहीं हटाया -- असंख्य अंगुलियां व्यर्थ में उन्हें दबाने के लिए उठती रही। आरंभ में, बटन उनके हटाने की लागत के कारण अपनी जगह बचे रहे। लेकिन इसका परिणाम इस रूप में भी हुआ कि निष्क्रिय बटन भी एक उद्देश्य पूरा करते लगे। इज़राइल में बेन-गुरियन यूनिवर्सिटी ऑफ़ द नेगेव की टाल ओरन-गिलाद का कहना है कि ऐसे पदयात्री जो बटन दबाते हैं, उनकी ग्रीन मैन निशान दिखाई देने से पहले सड़क पार करने की कम संभावना होती है। चौराहों पर व्यवहार का अध्ययन करने पर उन्होंने देखा कि वे लोग अधिक सहजता के साथ ऐसी प्रणाली का पालन करते हैं जो उनके इनपुट पर ध्यान देने का अभिप्राय रखती है। मिशिगन विश्वविद्यालय, एन आर्बर में मानव-कंप्युटर व्यवहार विशेषज्ञ ईटन अडार कहते हैं कि निष्क्रिय बटन इस तरह का प्लेसबो प्रभाव पैदा करते हैं क्योंकि लोगों को उनके द्वारा उपयोग की जा रही प्रणाली पर नियंत्रण करना पसंद होता है। डा. अडार नोट करते हैं कि उनके विद्यार्थी आमतौर पर क्लिक करने वाले "सहेजें" बटन के साथ सॉफ्टवेयर तैयार करते हैं जिसकी ऐसे उपयोगकर्ताओं को आश्वस्त करने के अलावा कोई भूमिका नहीं होती जिन्हें जानकारी नहीं है कि उनके कीस्ट्रोक स्वचालित रूप में सहेजे जाते हैं। उनका कहना है कि इसे मशीनी दुनिया में अंतर्निहित ठंडेपन के अहसास का सामना करने के लिए उदार धोखे के स्पर्श के रूप में विचार करें। यह एक दृष्टिकोण है। लेकिन, कम से कम सड़क चौराहों पर प्लेसबो बटनों का एक काला पहलू भी हो सकता है। ट्रेफिक प्रणालियों में मनोवैज्ञानिक कारकों का अध्ययन करने वाले वियना के संस्थान FACTUM के प्रमुख राल्फ़ रिज़र का मनना है कि पदयात्रियों की अपनी मौजूदगी के प्रति जागरूकता और धोखे के परिणामस्वरूप होने वाला आक्रोश अब उन लाभों से भारी पड़ता है। | Entry #25387 — Discuss  Winner Winner
|
कई वर्षों के बाद, इस बारे में कोई बड़ा झंझट किए बिना, न्यूयॉर्क में अधिकारियों ने उन नियंत्रण बटनों में से अधिकांश को अक्षम कर दिया जो कभी शहर में पैदल-पार लाइटों को संचालित करते थे। उन्होंने फैसला लिया कि कंप्यूटरीकृत टाइमर ने, लगभग हमेशा बेहतर काम किया है। 2004 तक, ऐसे 3,250 बटनों में से 750 से कम बटन कार्यरत थे। तथापि, शहरी प्रशासन ने, ऐसे निष्क्रिय बटनों को नहीं हटाया जिन्हें व्यर्थ में दबाने के लिए अनगिनत उंगलियां उठती है। शुरू में, इन्हें हटाने की लागत की वजह से बटन बच गए। लेकिन यह पता चला कि इस प्रकार के निष्क्रिय बटन भी एक उद्देश्य पूरा करते है। बटन दबाने वाले पैदल यात्री, जो बटन दबाते हैं, उनकी भी हरा आदमी दिखाई देने से पहले, क्रास करने की संभावना कम है। चोराहों पर व्यवहार का अध्ययन करने वाले इजरायल में, नेगेव के बेन-गुरियॉन विश्वविद्यालय के ताल ओरॉन कहते हैं। उसने नोट किया है कि लोग उस प्रणाली का अधिक आसानी से पालन करते है जिसका अभिप्राय उनके इनपुट को ध्यान में रखना होता है। निष्क्रिय बटन इस तरह का प्रयोगिक प्रभाव डालते है क्योंकि लोग, उपयोग की जा रही प्रणाली पर अपने नियंत्रण को पसंद करते है। मिशिगन विश्वविद्यालय, एन आर्बर में मानव-कंप्यूटर इंटरएक्टिव प्रभाव पर मानव विशेषज्ञ- एयतन अडार कहते हैं। डॉ अडार ने पाया है कि उनके छात्र आमतौर पर एक क्लिक "सहेजें" बटन के साथ सॉफ्टवेयर तैयार करते है, जिसकी आश्वासन के अलावा उन उपयोगकर्ताओं के लिए कोई भूमिका नहीं है जो अनजान है कि उनके कीस्ट्रॉक किसी तरह से स्वचालित रूप से सहेजे जा रहे है। वह कहते है कि इस मशीनी दुनिया में अंतर्निहित इस शीतलता का मुकाबला करने के लिए स्पर्श के इस परोपकारी उपाय के बारे में सोचो। यह एक पहलू है। परंतु, सड़क क्रॉसिंगों पर, प्रयोगिक बटनों का कम से कम एक ओर पहलू भी हो सकता है। विनीज़ संस्थान फैक्टौम(FACTUM), जोकि यातायात प्रणालियों में मनोवैज्ञानिक कारकों का अध्ययन करती है, के अध्यक्ष रॉल्फ रिस्सर का मानना है कि पैदल यात्रियों में उनके अस्तित्व के बारे में जागरूकता और धोखा होने के फलस्वरूप असंतोष के स्थान पर अब लाभ को बढ़ावा मिला है। | Entry #25103 — Discuss
|
बहुत सालों तक लगकर, इस बात को ज्यादा तूल ना देते हुए, न्यूयॉर्क के प्राधिकारियों ने ज्यादातर पैदल यात्री मार्ग प्रदर्शन संकेतों के नियंत्रण बटनों को निष्क्रिय कर दिया है जो पहले शहर में सक्रिय रहे थे। उन्होंने तय किया कि कंप्यूटरीकृत समयकों ने लगभग हमेशा ज्यादा प्रभावी कार्य किया है। 2004 तक 3250 में से 750 ही ऐसे बटन सक्रिय रहे। नगरीय सरकार ने हालांकि इन निष्क्रिय बटनों को हटाया नहीं- अनगिनत उंगलियों को बेकार में बटन दबाने का झंझट करना पड़ रहा है। पहले इन बटनों को अधिक खर्च की वजह से नहीं हटाया जा सका। पर बाद में पता चला निष्क्रिय बटन भी काम के हैं। पैदल यात्रियों की बिना हरा आदमी वाला संकेत देखे रोड़ पार करने की संभावना ना के बराबर है ये कहना है टाल ऑरोन-गिल्ड का बेन-गिरीयन विश्वविद्यालय , निगेव, इजरायल से। रास्ता पार करते समय के व्यवहार का अध्ययन करते समय उन्होंने, ध्यान दिया कि लोग ऐसे तंत्र को ज्यादा तत्परता से पालन करते हैं जो उनके इनपुट पर ध्यान देता है। निष्क्रिय बटन एक तरह से प्लेसीबो प्रभाव का काम करता है क्योंकि लोगों को ऐसे नियंत्रण वाले तंत्र की आदत सी हो गयी है जिसका वे प्रयोग करते आ रहे हैं। ये मानना है एन्न एडर, मानवीय- कंप्यूटर तालमेल के विशेषज्ञ, एन्न आर्बर विश्वविद्यालय, मिशीगन से । डॉ. एन्न एडर ने ध्यान दिया कि उनके विद्यार्थी सामान्यतः ऐसे क्लिकेबल 'सेव' बटनों का सॉफ्टवेयर डिजाइन करते हैं जिनका उपयोग केवल इतना है कि उन प्रयोगकर्ताओं को दिलासा दिलाने के लिए कि उनके कार्य को सहेज लिया गया है जबकि हर कुंजी स्ट्रोक अपने आप ही सहेजे जा रहे हैं इस बात से वे अनभिज्ञ हैं। इसको यूं मानिए एक हसीन छल जिससे मशीनी दुनिया के भावहीन कार्य संरचना से पार पायी जा सके। यह एक नजरीया भर हुआ। लेकिन रास्ता पार करने में, कम से कम प्लेसिबो बटनों के बुरे प्रभाव भी हो सकते हैं। राल्फ रिसर , एफ ए सी टी यू एम के प्रमुख , एक वियनी संस्थान जो यातायात तंत्रों में मनोवैज्ञानिक कारकों का अध्ययन करती है , मानते हैं कि पैदल यात्रियों को बटनों की जानकारी है एवं साथ ही छल के प्रति विरोध का होना, अब इस प्रभाव के लाभों को दरकिनार कर रहे हैं। | Entry #24797 — Discuss
|
कई वर्षों के दौरान न्यूयॉर्क में अधिकारियों ने इसके बारे में कोई बड़ी गड़बड़ किए बिना ज्यादातर नियंत्रण बटन बेकार कर दिए जो कभी शहर में पैदल यात्री-क्रॉसिंग लाइट को संचालित करते थे। उन्होंने तय किया था कि कम्प्यूटरीकृत टाइमर ने लगभग हमेशा ही बेहतर काम किया। 2004 तक, 3,250 में से कम से कम 750 ऐसे बटन हैं जो काम कर रहे हैं। हालांकि शहर की सरकार ने बेकार बटन को हटाया नहीं – यह इशारा करते हैं उन अनगिनत उंगलियों के प्रयास को जो बटन दबाने में व्यर्थ हुआ। प्रारंभ में उन्हें हटाने की लागत के कारण बटन बच गए। लेकिन यह पता चला कि बेकार बटन भी एक उद्देश्य को पूरा करते हैं। इज़राइल में नेग के बेन-गुरियन विश्वविद्यालय की ताल ओरोन-गिलाद कहती हैं कि ऐसे पैदल यात्री जो बटन दबाते हैं उनकी हरे रंग का आदमी दिखाई देने से पहले पार करने की संभावना कम होती है। क्रॉसिंग पर व्यवहार का अध्ययन करने के बाद वह नोट करती है कि लोग आसानी से एक ऐसी प्रणाली का पालन करते हैं जो उनके इनपुट पर ध्यान देती है। मिशिगन विश्वविद्यालय के एन-आर्बर में मानव-कंप्यूटर पारस्परिक प्रभाव के विशेषज्ञ ईटन एडर कहते हैं कि बेकार हुए बटन इस तरह के प्लेसबो प्रभाव को पैदा करते हैं क्योंकि लोग उन प्रणालियों पर नियंत्रण के प्रभाव को पसंद करते हैं जिनका वे उपयोग कर रहे हैं। डॉ एडर ने नोट किया कि उनके छात्र आमतौर पर एक क्लिक करने योग्य "सेव" बटन के साथ सॉफ्टवेयर डिजाइन करते हैं जिसकी कोई और भूमिका नहीं है सिवाय उन उपयोगकर्ताओं को आश्वस्त करने के अलावा जो इस बात से अनजान हैं कि उनके बटन दबाने वाले स्पर्श वैसे भी स्वचालित रूप से सहेजे जाते हैं। वह एक नजरिया है। लेकिन कम से कम रोड क्रॉसिंग पर प्लेसबो बटन में खामीयां भी हो सकती हैं। राल्फ़ रिज़र एक विनीज़ संस्थान में FACTUM के प्रमुख हैं जो यातायात प्रणालियों में मनोवैज्ञानिक कारकों का अध्ययन करते है, जोर देते हैं कि अब पैदल चलने वालों की अपने अस्तित्व के प्रति जागरूकता और धोखे के परिणामस्वरूप मिली नाराजगी लाभ को कम करती है। | Entry #25519 — Discuss
|
इधर कुछ सालों से, बगैर किसी झमेले के, न्यू यॉर्क में जिम्मेदार विभाग द्वारा शहर में सड़कों व चौराहों पर लगे पैदल सड़क पार करने के लिए स्वयं लोगों द्वारा संचालित बत्तियों के बटनों को निष्क्रिय कर दिया गया है। कम्प्यूटरीकृत संचालन, उन्होंने तय किया, हर हाल में बेहतर साबित होता है। वैसे, नगर प्रशासन ने उन निष्क्रिय बटनों को हटाया भी नहीं, जिसके चलते असंख्य उंगलियां अभी भी उनको निरर्थक दबाती-फिरती हैं। शुरू में तो उन्हें उतारने-हटाने के खर्च के कारण वे बटन रखे गए, लेकिन फिर देखा गया की निष्क्रिय बटन भी एक उद्देश्य पूरा करते हैं। इजराइल के नेगेव शहर में बेन-गुरियन विश्वविद्यालय के तल ओरों-गिलाद कहती हैं कि पैदल चलने वाले, जो बटनों का इस्तेमाल करते हैं, वे जब तक सामने की बत्ती हरी न हो जाए, कम ही सड़क पार करते हैं। चौराहों पर लोगों के व्यवहार का अध्धयन करते हुए उन्होंने पाया कि लोग अमूमन ऐसी प्रणाली के प्रति स्वतः ही आज्ञाकारी होते हैं जो उन्हें लगता हैं कि उनकी ही अपनी किसी क्रिया पर आधारित है। ऐसे में, अन्न आर्बर स्थित मिशिगन विश्वविद्यालय में मानव-कंप्यूटर अंतक्रिया के विशेषयज्ञ ऑयटन अदर का कहना है की निष्क्रिय कर दिए गए बटनों का भी "प्लेसबो" (अर्थात, वास्तविक न भी सही पर मनोवैज्ञानिक) प्रभाव तो पड़ता ही है कि लोगों को, वे जिन यंत्रों का इस्तेमाल करते हैं, उन पर उनका नियंत्रण ये, ये एहसास अच्छा लगता है। डॉ अदर बताते हैं कि उनके छात्र "सहेजें" के लिए अक्सर ऐसे दबाने वाले बटनों के सॉफ्टवेयर प्रारूप तैयार करते हैं जिनका उपयोग कुछ होता नहीं सिवाय उन उपयोगकर्ता को आश्वस्त करने के जो इस बात से बेखबर हैं कि कंप्यूटर पर उनके द्वारा काम तो स्वतः ही सहेजा जा रहा है। वे कहते हैं कि इसे मशीनीकृत दुनिया की अन्तर्निहित उदासीनता के खिलाफ एक उदार छल की तरह सोचा जाए। यह हुआ एक दृष्टिकोण। लेकिन कम से कम चौराहों पर इस तरह के "प्लेसबो" बटनों का एक खतरनाक पहलू भी हो सकता है। यातायात प्रणालियों में मनोवैज्ञानिक कारकों पर अध्ययन कर रही वियतनामी संस्थान, एफ.ए.सी.टी.यू.एम. (फैक्टम) के प्रमुख राल्फ रिस्सर का मानना है कि पैदल वालों को बटनों की मौजूदगी का पता होना और तब इस बात का भी एहसास कि उनको लेकर उनके साथ एक धोखा किया गया है, उससे जो रोष उनमे पैदा होता है, वह उन बटनों के फायदों से अब कहीं अधिक नुकसानदेह होने लगा है। | Entry #25027 — Discuss
|
कई वर्षों के दौरान, इसके बारे में कोई बड़ा हलचल किए बिना, न्यूयॉर्क में अधिकारियों ने ज्यादातर नियंत्रण बटन को निष्क्रिय कर दिया जो एक बार शहर में पैदल यात्री मार्ग पर लाइट संचालित करते थे। कम्प्यूटरीकृत टाइमर, उन्होंने फैसला किया था, लगभग हमेशा बेहतर काम किया। 2004 तक, 3,250 से कम 750 ऐसे बटन कार्यात्मक बने हुए हैं। हालांकि, शहर सरकार ने विकलांग बटन को दूर नहीं किया है-अनगिनत उंगलियां निरर्थक दबाने के लिए। प्रारंभ में, बटन उन्हें हटाने की लागत के कारण बच गए। लेकिन यह पता चला कि निष्क्रिय बटन भी एक उद्देश्य पूरा करते हैं। हरे रंग का आदमी दिखाई देने से पहले एक बटन दबाने वाले पैदल यात्रियों को पार करने की संभावना कम होती है, इज़राइल में बेन-गुरियन यूनिवर्सिटी ऑफ़ द नेगेव के ताल ओरण-गिलाद कहते हैं। क्रॉसिंग पर व्यवहार का अध्ययन करने के बाद, वह नोट करती है कि लोग अधिक तत्परता से एक ऐसी प्रणाली का पालन करते हैं जो उनके इनपुट पर ध्यान देती है। निष्क्रिय बटन इस तरह के प्लेसबो प्रभाव पैदा करते हैं क्योंकि लोग उन प्रणालियों पर नियंत्रण की धारणा पसंद करते हैं जो वे उपयोग कर रहे हैं, मिशिगन विश्वविद्यालय के एन-आर्बर में मानव-कंप्यूटर इंटरैक्शन के विशेषज्ञ ईटन अडार कहते हैं। डॉ अडार ने नोट किया कि उनके छात्र आमतौर पर एक क्लिक करने योग्य "सेव" बटन के साथ सॉफ्टवेयर डिजाइन करते हैं जिसमें उन उपयोगकर्ताओं को आश्वस्त करने के अलावा कोई भूमिका नहीं है जो इस बात से अनजान हैं कि उनके कीस्ट्रोक्स वैसे भी स्वचालित रूप से सहेजे जाते हैं। इसके बारे में सोचो, वह कहते हैं, मशीन की दुनिया की अंतर्निहित शीतलता का मुकाबला करने के लिए परोपकारी धोखे के स्पर्श के रूप में। वह एक नजरिया है। लेकिन, सड़क क्रॉसिंग पर कम से कम, प्लेसीबो बटन में गहरा पक्ष भी हो सकता है। राल्फ़ रिज़र, फैक्टम के प्रमुख, एक विनीज़ संस्थान जो ट्रैफ़िक सिस्टम में मनोवैज्ञानिक कारकों का अध्ययन करता है, अपने अस्तित्व के बारे में पैदल चलने वालों की जागरूकता पर ध्यान दें, और धोखे में परिणामी आक्रोश, अब लाभ पल्ला झुक रहा है। | Entry #24850 — Discuss
|
कई वर्षों के दौरान, इसके बारे में कोई बड़ा उपद्रव किए बिना, न्यूयॉर्क में अधिकारियों ने अधिकांश नियंत्रण बटन अक्षम कर दिए, जो एक बार शहर में पैदल यात्री-क्रॉसिंग लाइटों का संचालन करते थे। कम्प्यूटरीकृत टाइमर, उन्होंने तय किया था, लगभग हमेशा बेहतर काम किया। 2004 तक, 3,250 से कम ऐसे बटन कार्यात्मक रहे। हालांकि, शहर की सरकार ने अक्षम बटन को दूर नहीं किया - अनगिनत उंगलियों को निरर्थक दबाने के लिए। प्रारंभ में, बटन उन्हें हटाने की लागत के कारण बच गए। लेकिन यह पता चला कि निष्क्रिय बटन भी एक उद्देश्य की पूर्ति करते हैं। हरे रंग का आदमी दिखाई देने से पहले एक बटन दबाने वाले पैदल यात्रियों को पार करने की संभावना कम होती है, इज़राइल में बेन-गुरियन यूनिवर्सिटी ऑफ़ नेगेव के ताल ओरण-गिल्ड कहते हैं। क्रॉसिंग पर व्यवहार का अध्ययन करने के बाद, वह नोट करती है कि लोग अधिक आसानी से एक प्रणाली का पालन करते हैं जो अपने इनपुट पर ध्यान देता है। इनऑपरेटिव बटन इस तरह के प्लेसेबो प्रभाव पैदा करते हैं क्योंकि लोग उन प्रणालियों पर नियंत्रण की छाप पसंद करते हैं, जो मिशिगन विश्वविद्यालय के एन-अर्बोर में मानव-कंप्यूटर इंटरैक्शन के विशेषज्ञ ईटन अडार कहते हैं। डॉ। अदार ने नोट किया कि उनके छात्र आमतौर पर एक क्लिक करने योग्य "सेव" बटन के साथ सॉफ्टवेयर डिजाइन करते हैं जिसमें उन उपयोगकर्ताओं को आश्वस्त करने के अलावा कोई भूमिका नहीं है जो इस बात से अनजान हैं कि उनके कीस्ट्रोक्स वैसे भी स्वचालित रूप से सहेजे जाते हैं। इसके बारे में सोचो, वह कहते हैं, मशीन की दुनिया की अंतर्निहित शीतलता का मुकाबला करने के लिए परोपकारी धोखे के स्पर्श के रूप में। वह एक नजरिया है। लेकिन, रोड क्रॉसिंग पर कम से कम, प्लेसबो बटन का गहरा हिस्सा भी हो सकता है। राल्फ रिज़र, फैक्टम के प्रमुख, एक विनीज़ इंस्टीट्यूट जो ट्रैफ़िक सिस्टम में मनोवैज्ञानिक कारकों का अध्ययन करता है, यह मानता है कि पैदल चलने वालों को अपने अस्तित्व के बारे में जागरूकता है, और धोखे पर परिणामस्वरूप नाराजगी, अब लाभ से आगे निकल जाता है। | Entry #25052 — Discuss
|
कई वर्षों से बिना किसी बड़ी गड़बड़ी के , न्यूयॉर्क के प्राधिकारियों ने अधिकांश नियंत्रण बटन को, जो शहर में पैदल यात्री-क्रॉसिंग लाइटों का संचालन करने के लिए इस्तेमाल किए जाते थे उन्हें निष्क्रिय कर दिया है। उन्होंने कम्प्यूटर द्बारा जो समय तय किया था, उसने लगभग हमेशा बेहतर तरह से काम किया है। 2004 तक 3,250 में से 750 से भी कम बटन क्रियाशील रहे। हालांकि, शहर की सरकार ने निष्क्रिय बटन को हटाया नहीं। प्रारंभ में, बटन हटाने की लागत के कारण वह बच गए। लेकिन यह पता चला कि निष्क्रिय बटन भी किसी न किसी उद्देश्य की पूर्ति करते हैं। इजराइल में बेन-गुरियन यूनिवर्सिटी ऑफ नेगेव की ताल ओरण-गिल्ड कहती हैं कि पैदल यात्री जो एक बटन दबाकर रास्ता पार करना चाहते हैं, उनमें यह सम्भावना बहुत कम होती है कि वह हरे रंग का आदमी दिखाई देने से पहले रास्ता पार करें। क्रॉसिंग पर व्यवहार का अध्ययन करते हुए उन्होंने पाया कि लोग अधिक आसानी से किसी प्रणाली का पालन करते हैं जो उनपर ध्यान देते हैं। मिशिगन विश्वविद्यालय के एन-अर्बोर में मानव-कंप्यूटर इंटरैक्शन के विशेषज्ञ ईटन अडार कहते हैं कि निष्क्रिय बटन, प्लेसेबो प्रभाव पैदा करते हैं क्योंकि लोग उन प्रणालियों पर नियंत्रण पसंद करते हैं जो वह इस्तेमाल करते हैं। डॉ. अदार ने ध्यान दिया कि उनके छात्र आमतौर पर एक क्लिक करने योग्य "सेव" बटन के साथ सॉफ्टवेयर डिजाइन करते हैं जिसका कार्य केवल उन उपयोगकर्ताओं को आश्वाशन देने के अलावा और कुछ नहीं है, जो इस बात से अनजान हैं कि उनके कीस्ट्रोक्स वैसे भी स्वचालित रूप से सहेजे जाते हैं। वह कहते हैं कि इस बारे में सोचें कि मशीन की दुनिया में अंतर्निहित मुकाबला करने के लिए यह केवल एक धोखा है। वह एक नजरिया है। लेकिन, रोड क्रॉसिंग पर कम से कम, प्लेसबो बटन का गहरा पक्ष भी हो सकता है। राल्फ रिज़र, फैक्टम के प्रमुख, विनीज़ इंस्टीट्यूट जो ट्रैफ़िक सिस्टम में मनोवैज्ञानिक कारकों का अध्ययन करता है, यह मानता है कि अपने अस्तित्व के बारे में पैदल चलने वालों की जागरूकता बहुत कम है और इसी धोखे के परिणामस्वरूप नाराजगी को देखते हुए, अब लाभ से आगे निकल गए हैं। | Entry #24940 — Discuss
|
ProZ.com translation contests
ProZ.com translation contests offer a fun way to take a break from your normal routine while testing and honing your skills with fellow translators.
Contests overview
Professional translators (and some novices) take part in ProZ.com translation contests for fun, friendly competition and prizes.Propose a source text
Suggest and provide feedback on source texts for upcoming contests.Winners
See who has won previously.Statistics
See contest statistics.ProZ.com Translation Contests. Patent pending.


 Likes (
Likes ( Dislikes (
Dislikes (


